|
This article [J. Med. Imag. 4(1), 014505 (2017)] was originally published with the captions for Figs. 8 and 9 transposed. The captions and figures below are correctly matched. Fig. 8Stress distributions obtained using the hyperelastic Arruda–Boyce model for Abaqus (a) at the front surface, (b, c, d) 3-D stress distribution along (b) the -direction , (c) -direction , (d) and -direction with indenter positioned on top of inhomogeneity, (e) 3-D stress distribution along -direction with indenter positioned in 10 mm distance to inhomogeneity. 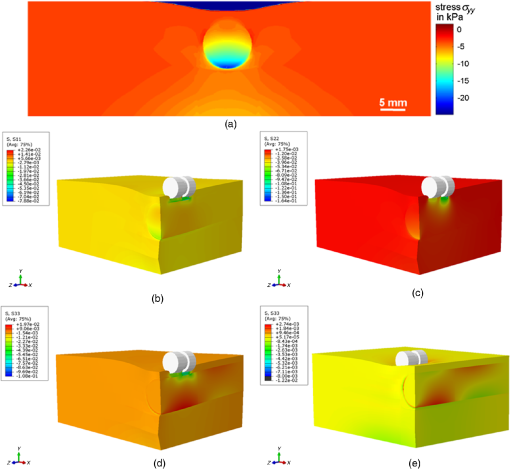 Fig. 9Flow chart and results for obtained displacements fields with and without foreign body, the resulting difference displacement field, the calculate strain field, and corresponding cross-section plot, which compares the difference approach strain field with the conventional results shown in Fig. 7(b). 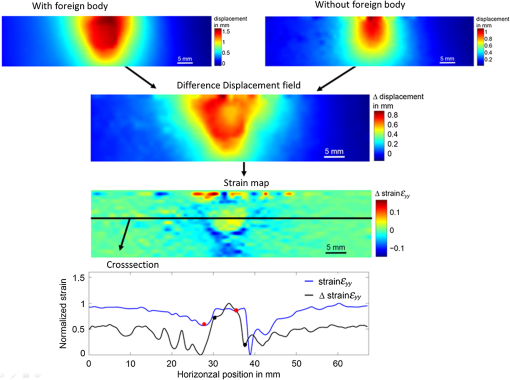 This article was corrected online on 23 May 2017. |
CITATIONS
Cited by 4 scholarly publications.
Tissue optics
Biomedical optics
Digital image correlation
Elastography
Soft tissue optics
3D modeling
Medical imaging

